2020. 1. 25. 04:03ㆍ카테고리 없음

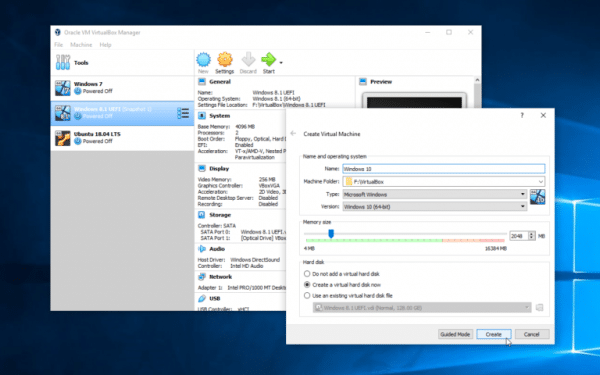
- Jul 4, 2018 - Software tools that divide and conquer operating systems. Boot Camp is Apple's free tool for running a Virtual session under macOS, but.
- Virtualization utilities let you run a complete Windows system on a Mac or Linux machine, or one version of Windows inside another version. The virtual machine created by the software acts like a real desktop or laptop computer for the guest operating system to run on, except that it doesn't require extra hardware.
This article needs to be updated. Please update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. ( October 2017) Solaris network virtualization and resource control is a set of features originally developed by as the Crossbow umbrella project, providing an internal and framework within the. Major features of the Crossbow project include:.
Virtualization Tools For Windows
Virtual NIC pseudo-network interface technology. Exclusive IP zones.
QEMU is frequently the hypervisor of choice for Linux users, based on its zero-dollar price tag and easy-to-master full-system emulation tools. The open source emulator simulates an impressive range of hardware peripherals, using dynamic translation for ideal performance.
Bandwidth management and flow control on a per interface and per VNIC basis. Contents. Description The Crossbow project software, combined with next generation network interfaces like xge and bge, enable and resource control for a single system. By combining VNICs with features such as or the hypervisor, system administrators can run applications on separate to improve performance and provide security. Resource management and flow control features provide and for packet flows on separate virtual machines.
You can allocate bandwidth amounts and manage data flows not only for the physical network interface but also for any containers configured on the interface. The Crossbow resource control features enable increased system efficiency and the ability to limit the amount of bandwidth consumed by a process or virtual machine. Features of the Crossbow project This section briefly describes the main features of the Crossbow network virtualization and resource control project. For further details on each feature, see the Oracle Solaris 11 Network Virtualization and Network Resource Management white paper. VNIC A VNIC is a pseudo network interface that is configured on top of a system's physical, also called a network interface (NIC). A physical interface can have more than one VNIC. Each VNIC operates like and appears to the system as a physical NIC.
The individual VNIC is assigned a media access control address , which can be configured to a value other than the default MAC address assigned to the physical NIC. You can use the resource control features of Crossbow to allocate separate bandwidths to the individual VNICs.

Moreover, you can configure a virtual machine, such as an exclusive IP zone or xVM domain on top of a VNIC. Virtual switch When the first VNIC is created on a system, a virtual switch is also created above the physical interface. Though not directly accessible to the user, the virtual switch provides connectivity between all VNICs configured on the same physical interface, enabling the virtual network in a box scenario. The virtual switch forwards packets between the system's VNICs. Thus, packets from an internal VNIC source never have to pass to the external network to reach an internal network destination. Exclusive IP zones An is a separate instance of a full TCP/IP stack, which functions as a.
Enable Virtualization Mac
Each exclusive IP zone is built upon a physical network interface and has its own IP-related state. IP instances support DHCPv4 and IPv6 address autoconfiguration. An exclusive IP zone can have its own routing table and routing protocols separate from the global zone on a system. Moreover, a system administrator can run the ifconfig command within an exclusive IP instance to set up a logical interface within the exclusive IP zone. Modifications to the TCP/IP MAC layer In Solaris, the MAC layer is part of the larger of the TCP/IP protocol stack.
The Crossbow project modifies this layer with several new features, including the MAC client interface. This virtual entity is a kernel data structure that is not externally visible to the system administrator. However, the MAC client interface along with the VNIC driver provides the VNIC functionality in OpenSolaris. Additionally, Crossbow modifications to the MAC layer enable a system administrator to assign a different MAC address to each VNIC on a system.
Define System Tools
Resource management and flow control The Crossbow project features provide bandwidth management and flow control on a per VNIC basis. A system administrator can configure different bandwidth allocations to the various VNICs on a host through the new Crossbow-related commands. Traffic through each VNIC can be classified and separated into individual flows, based on port number, destination IP address, and other parameters. These features can be used to improve system efficiency and enable differentiated services for separate VNICs.
Observability features Standard Solaris observability tools can be used to monitor the status of exclusive IP instances, VNICs, and virtual machines running on VNICs. For example, familiar tools such as and can report status on the operations of a VNIC. Additionally, the command has been extended for Crossbow to report statistics on packet flows defined with the flowadm command. Feature and code availability The exclusive IP zones feature was first introduced in the 10 8/07 release.
The first version of the Crossbow feature set was incorporated in 2009.06. The full Crossbow feature set became part of Solaris with the 2011 release of Solaris 11.
Oracle discontinued the OpenSolaris download sites after its, but source code for Crossbow can be downloaded from the sites of the derivatives of (see ). See also. References. Archived from on 2009-10-21.
November 2011. Retrieved 2017-10-27. Belgaied, Kais and Lu, Roamer. Droux, Nicolas,.
Rami, Rosen,. Rami, Rosen,. Moellenkamp, Joerg. Moellenkamp, Joerg External links. Archived from on 2009-10-21. The project page for OpenSolaris Crossbow, which includes technical specifications, documentation and latest news about the project. Links for the most current dladm man pages, which is one of the main tools used to manage virtual network resources.
